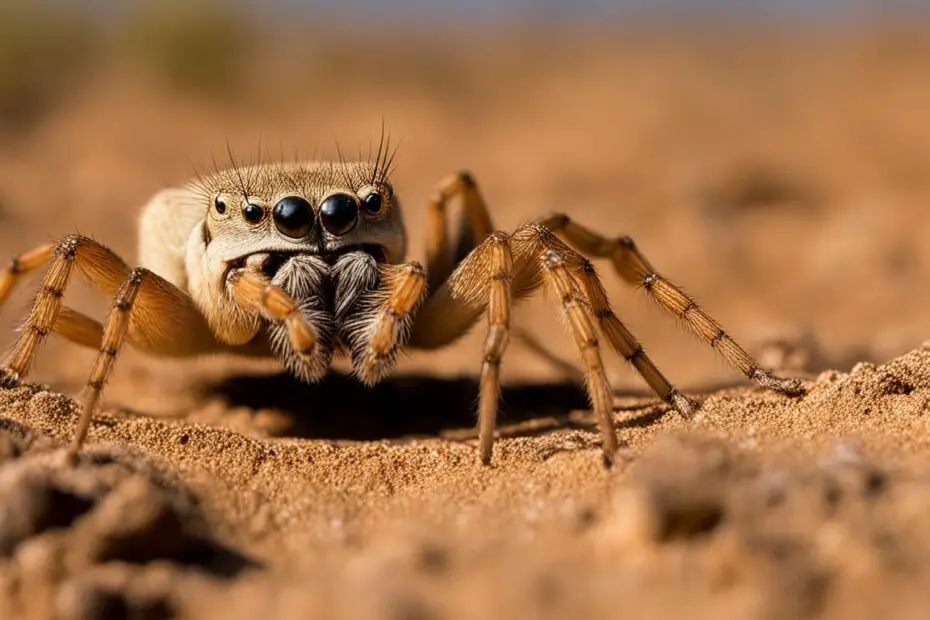
Camel spiders, also known as wind spiders or sun spiders, have long been surrounded by myths and misconceptions that have fueled fear and misunderstanding. Many people wonder, are camel spiders dangerous? In this article, we will delve into the facts to unveil the truth about these intriguing arachnids and separate fact from fiction.
Contrary to popular belief, camel spiders are not venomous and do not possess any venom glands. Therefore, their bites are not toxic and do not pose a significant threat to humans. Understanding the behavior, habitat, and bite symptoms of camel spiders can help dispel the myths and provide a clearer picture of their actual danger level.
Key Takeaways:
- Camel spiders are not venomous and do not pose a significant danger to humans.
- Understanding their behavior, habitat, and bite symptoms can help dispel myths and misconceptions.
- Camel spiders are fascinating creatures that are found primarily in desert regions.
- They are not aggressive towards humans and prefer to be left alone.
- Exercise caution and avoid provoking camel spiders to minimize the risk of being bitten.
What are Camel Spiders?
Camel spiders, scientifically known as Solifugae, are fascinating creatures that display characteristics of both spiders and scorpions, although they belong to neither group. They are from a group of bugs called Solpugids. These arachnids are found primarily in dry and sandy desert regions, including the Middle East.
One of the intriguing aspects of camel spiders is their size. They can range from a few millimeters to around 15 centimeters in length, including their legs. This wide size variation contributes to the myths and misconceptions surrounding these creatures. Despite their intimidating appearance, camel spiders are not as large as exaggerated descriptions often imply.
Camel spiders have distinct features that set them apart. Their large jaws resemble pliers, and they possess three pairs of hairy legs, making them visually striking. However, it’s important to remember that their unique appearance does not necessarily indicate danger or aggression.
To better understand camel spiders, it’s crucial to explore their natural habitat and behavior. These arachnids thrive in arid environments, where they have adapted to survive in extremely dry and sandy conditions. Their ability to survive in such harsh environments is a testament to their resilience and evolutionary adaptations.
Camel spiders are primarily active during the night, seeking shelter in burrows or crevices during the scorching daytime temperatures. They are solitary creatures and generally avoid contact with humans unless provoked or threatened. Despite their reputation for being aggressive, camel spiders prefer to engage with their natural environment and prey rather than interact with humans.
| Attribute | Information |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Solifugae |
| Size | Ranges from a few millimeters to around 15 centimeters in length, including legs |
| Habitat | Dry and sandy desert regions, particularly in the Middle East |
| Behavior | Nocturnal, solitary, and primarily avoids contact with humans |
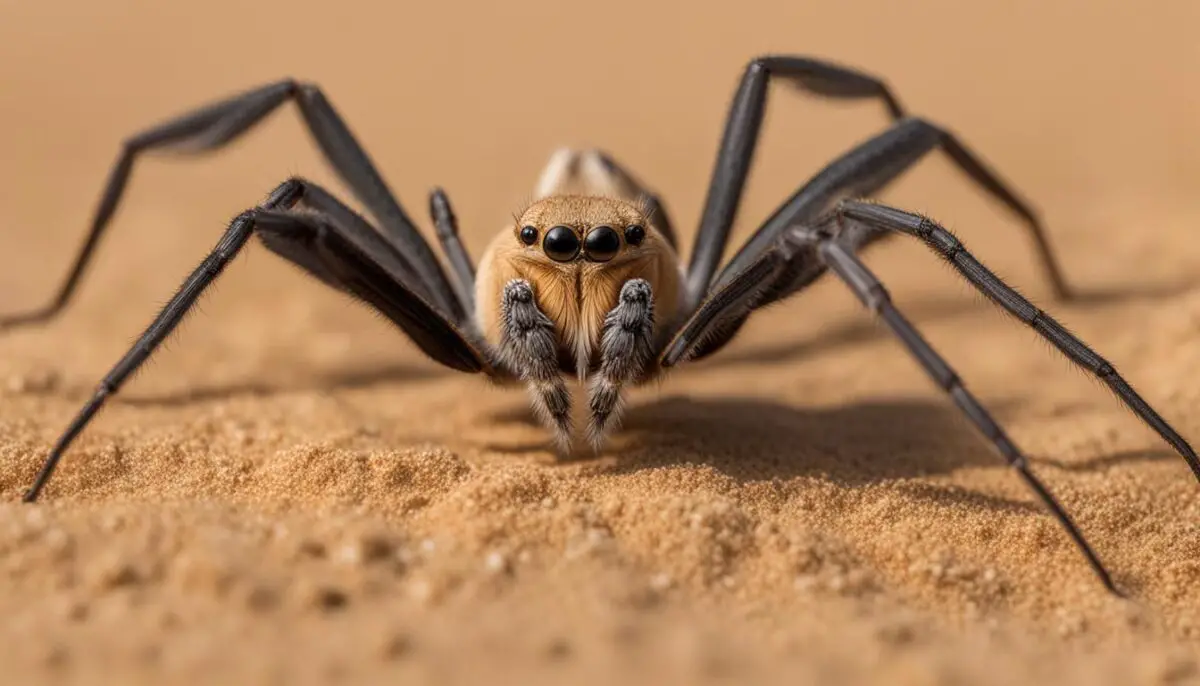

Understanding the true nature of camel spiders can help dispel the myths and misconceptions surrounding these creatures. They are not the monstrous, venomous creatures often portrayed in popular culture.
“The more we learn about camel spiders, the more we realize they are fascinating creatures adapted to thrive in their unique desert habitats. They play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of desert ecosystems.”
By separating fact from fiction and dispelling the common misconceptions surrounding camel spiders, we can foster a greater appreciation for the uniqueness and importance of these arachnids in their natural environments.
Debunking Camel Spider Myths
Over the years, various myths and legends have circulated about camel spiders, fueling fear and misconceptions. These arachnids, commonly known as wind spiders or sun spiders, have been the subjects of exaggerated tales portraying them as highly venomous and aggressive creatures. However, it is crucial to separate fact from fiction to understand the reality of camel spiders and dispel these myths.
Myth #1: Camel spiders grow to an exaggerated size: One of the most persistent myths surrounding these creatures is their supposed gigantic size. While camel spiders can be intimidating in appearance, they do not grow as enormous as often described. The average size of a camel spider ranges from a few millimeters to around 15 centimeters in length, including their legs. Contrary to the myth, these arachnids are not monstrous giants.
Myth #2: Camel spiders possess supernatural speed and jumping abilities: Another commonly perpetuated myth is the belief that camel spiders possess incredible speed and extraordinary jumping abilities. In reality, their speed has been exaggerated, leading to misconceptions about their agility. While camel spiders can move quickly, they do not possess any extraordinary speed or jumping capabilities beyond what is expected for their size.
Myth #3: Camel spiders eat the stomachs of camels: One particularly imaginative myth that has circulated is the belief that camel spiders feast on the stomachs of camels. However, this notion is entirely false. Camel spiders are predatory hunters that primarily prey on small insects, spiders, scorpions, and occasionally lizards. They do not consume the stomachs of camels or engage in such unusual feeding behavior.
Myth #4: Camel spiders inject anesthesia while feeding: A myth often tied to their feeding behavior is the belief that camel spiders inject anesthesia into their prey, inducing numbness and preventing the prey from feeling pain. This notion is purely fictional. Camel spiders do not possess any mechanism to inject anesthesia into their prey while feeding. Instead, they rely on their powerful jaws and digestive enzymes to consume their prey.
The Reality of Camel Spiders
By addressing these prevalent myths, it becomes clear that camel spiders are not the terrifying creatures they are often portrayed as. They are fascinating arachnids with unique physical attributes and behaviors, but their size, speed, feeding habits, and hunting techniques have been significantly exaggerated over time. Understanding the truth about camel spiders can help dispel unwarranted fear and foster a greater appreciation for these resilient creatures in their natural habitat.
Camel Spider Myths vs. Reality
The table below presents a comparison between the common myths associated with camel spiders and the corresponding realities.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Camel spiders grow to an enormous size. | Camel spiders typically range from a few millimeters to around 15 centimeters in length, including their legs. |
| Camel spiders possess supernatural speed and jumping abilities. | While camel spiders can move quickly, their speed and jumping abilities are not extraordinary and are within the range of their size. |
| Camel spiders eat the stomachs of camels. | Camel spiders are predatory hunters that primarily prey on insects, spiders, scorpions, and occasionally lizards. They do not consume the stomachs of camels. |
| Camel spiders inject anesthesia while feeding. | Camel spiders do not possess the ability to inject anesthesia into their prey. They rely on their jaws and digestive enzymes to consume their prey. |
Understanding the realities dispels these myths and provides a clearer insight into the true nature of camel spiders.
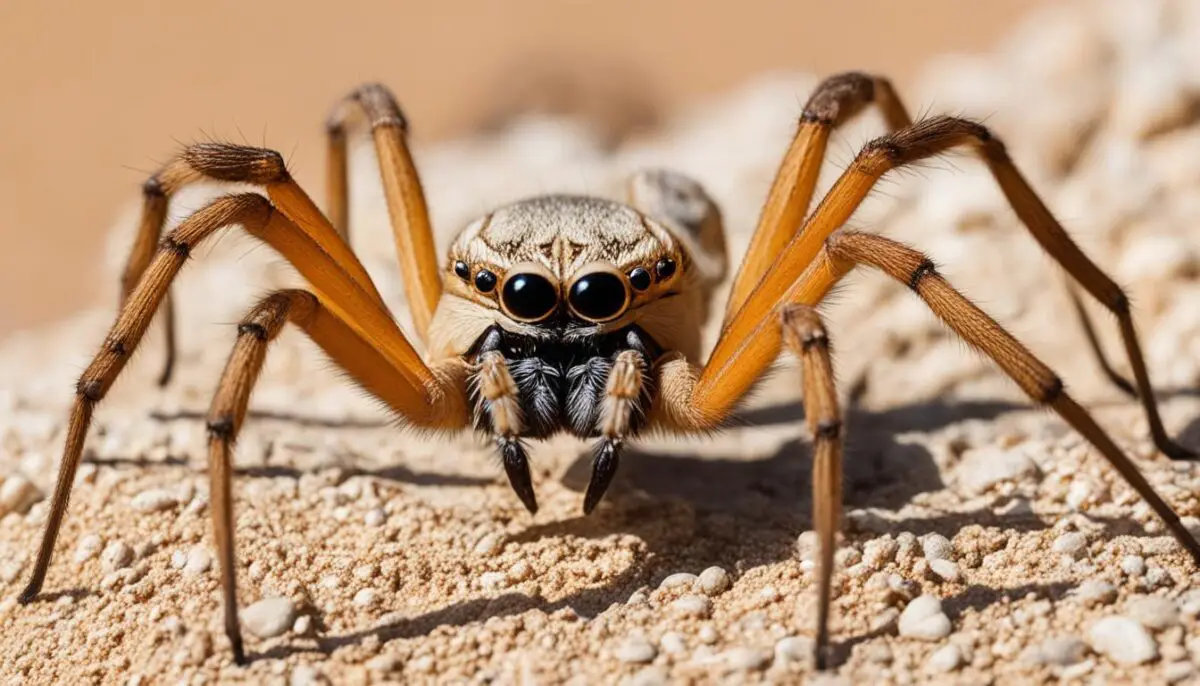

Understanding Camel Spider Bites
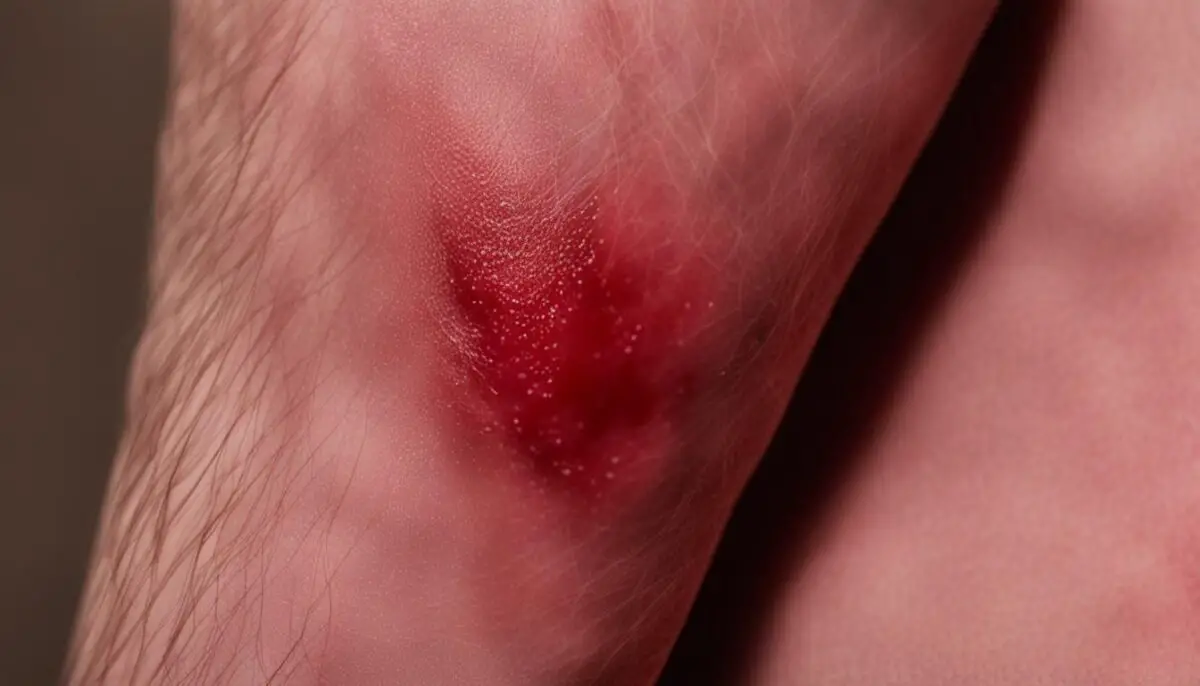
While camel spiders are not venomous, they are capable of biting humans if they feel threatened. These creatures have large, plier-like jaws that can inflict a painful bite.
The bite of a camel spider can result in mild to severe bleeding, swelling, and pain. It is essential to exercise caution and avoid provoking these creatures to minimize the risk of being bitten. Generally, camel spider bites are relatively rare, with occurrences typically happening when humans come into direct contact with the spiders.
Recognizing the symptoms of camel spider bites is crucial for prompt identification and appropriate response. Some common bite symptoms include:
- Bleeding
- Swelling
- Pain
| Camel Spider Bite Symptoms | Camel Spider Behavior |
|---|---|
| Bleeding | Camel spiders are primarily nocturnal and solitary creatures. |
| Swelling | They are known for their impressive speed and agility. |
| Pain | Camel spiders prey on insects, small animals, and even other spiders. They are opportunistic feeders and search for food during the night. |
If you suspect that you have been bitten by a camel spider, it is advisable to clean the wound gently with soap and water. Applying an antiseptic ointment and covering the bite with a clean bandage can help prevent infection. If the symptoms worsen or persist, it is crucial to seek medical attention.
Remember, understanding camel spider bite symptoms and taking appropriate measures can help mitigate potential risks associated with encounters with these creatures.
Evaluating the Danger of Camel Spiders
While there is a perception that camel spiders are highly dangerous, it is crucial to understand the actual level of threat they pose to humans. Contrary to popular belief, camel spiders are not a significant danger and are unlikely to cause severe harm. Although their bites can be painful and may lead to mild bleeding, swelling, and discomfort, it is important to note that camel spiders are not venomous and do not pose a lethal threat.
Camel spiders are aggressive hunters, equipped with powerful jaws to capture and feed on small prey such as insects and lizards. However, they typically avoid contact with humans and prefer to be left alone. It is vital to respect their natural behavior and maintain a safe distance when encountering them in their habitat.
“Camel spiders are often misunderstood and unfairly portrayed as dangerous creatures. In reality, they are just trying to survive in their environment,” says Dr. Sarah Thompson, Arachnologist at the University of Nevada.
Camel Spider Bite Symptoms
In the rare event that a camel spider bites a human, it is crucial to identify and address the symptoms promptly. Common bite symptoms include:
- Painful bite with mild to severe bleeding
- Localized swelling and redness
- Discomfort and tenderness at the bite site
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms after a camel spider bite, it is advisable to seek medical attention to ensure proper wound care and prevent any potential infections.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Camel spiders inject anesthesia while feeding | Camel spiders do not inject anesthesia |
| Camel spiders grow to gigantic sizes | Camel spiders do not exceed a certain size limit |
| Camel spiders eat the stomachs of camels | Camel spiders do not consume camel stomachs |
By understanding the actual threat level posed by camel spiders and debunking the misconceptions surrounding them, individuals can alleviate unnecessary fear. It is important to stay informed, take appropriate precautions, and coexist with these fascinating creatures without undue concern.
Conclusion
In conclusion, camel spiders, also known as wind spiders or sun spiders, may appear daunting due to their size and appearance, but they are not venomous and do not pose a significant threat to humans. It is important to separate fact from fiction when it comes to understanding these creatures.
By debunking the myths surrounding camel spiders and understanding their behavior, habitat, and bite symptoms, we can alleviate unnecessary fear. Camel spiders are not aggressive towards humans, and it is best to exercise caution, avoid provoking them, and allow them to continue their natural behavior without disturbance.
To protect yourself from camel spiders, it is recommended to stay informed about their behavior and take appropriate precautions. If you come across a camel spider, remember that they are not dangerous and prefer to be left alone. By respecting their natural habitat and avoiding unnecessary interaction, we can coexist peacefully with these fascinating arachnids.
FAQ
Are camel spiders dangerous?
No, camel spiders are not dangerous to humans. They do not possess venom and do not pose a significant threat.
What is the size of camel spiders?
Camel spiders can range in size from a few millimeters to around 15 centimeters in length, including their legs.
Where do camel spiders live?
Camel spiders primarily inhabit dry and sandy desert regions, such as the Middle East.
Do camel spiders have venom?
No, camel spiders do not possess venom. They are not venomous creatures.
What are some facts about camel spiders?
Camel spiders, also known as wind spiders or sun spiders, belong to a group of arachnids called Solifugae. They have large jaws resembling pliers and three pairs of hairy legs.
Are there any myths surrounding camel spiders?
Yes, there are myths surrounding camel spiders, such as their exaggerated size, exaggerated behavior, and alleged ability to eat camel stomachs. These myths are not true.
What are the symptoms of a camel spider bite?
Camel spider bites can cause mild to severe bleeding, swelling, and pain.
How dangerous are camel spider bites?
While camel spider bites can be painful, they are not venomous and do not pose a significant danger to humans.
How can I protect myself from camel spiders?
To protect yourself from camel spiders, it is best to exercise caution, avoid provoking them, and allow them to continue their natural behavior without disturbance.

